What is an animation pipeline?
An animation pipeline is a structured workflow used to manage the complex process of creating animated films, series, or advertisements. It ensures efficiency, organization, and quality from the initial concept to the final output.
Key components of CGI animation pipeline
CGI (Computer-Generated Imagery) animation requires a multi-stage pipeline involving pre-production, production, and post-production. Each phase has a dedicated team and tools to streamline the entire process.
What is pre-production in the animation pipeline?
Pre-production is where all the planning happens. It lays the foundation for the animation project.
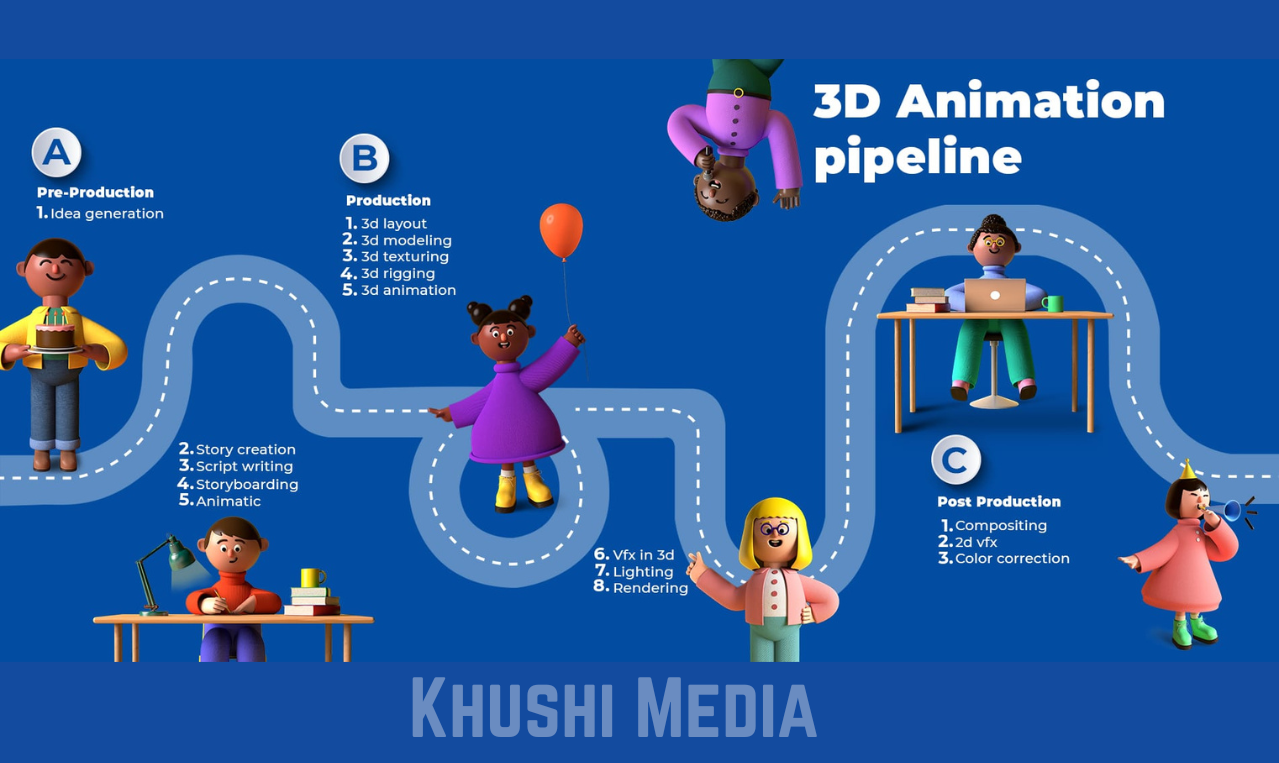
3D animation production pipeline has three main stages:
- Pre-production
- Production
- Post-production
Based on organizational considerations, resources, outcomes, and other factors, each segment of the 3D animation industry uses the three stages a little differently, but the main structure remains intact.
Pre-production consists of the following steps:
Idea Generation:
This is the brainstorming stage where teams generate multiple ideas, themes, or storylines.
Story Creation:
Selected ideas are developed into detailed stories with strong characters, themes, and arcs.
Script Writing:
Writers convert the story into a formal script, including dialogue, scenes, and transitions.
Storyboarding:
A storyboard is a series of sketches or panels that visually represent the script. It helps visualize the flow of the story.
Animatic:
An animatic is a rough animated version of the storyboard with temporary sound. It helps determine timing and pacing.
Design:
Character designs, props, environments, and visual styles are finalized here. These assets are passed to the production team.
What is the 3D animation production process?
Production is where the actual animation work begins using specialized 3D software.
At this stage, visual elements of the 3D animation will be handed out to the designated teams and artists. Team leaders make sure time frames, and quality matches those of the determined plan in the pre-production stage and goes as smoothly as possible. The outcome of this stage shapes the entirety of the 3D animation.
The production stage consists of the following steps:
3D Layout:
Layouts define camera angles, character placement, and rough movement paths for scenes. The 3D layout contains basic 3D attributes such as the characters’ size, shape, environment, a simple animation of the characters, proxy geometry, etc.
3D Modeling:
3D modeling is the process of developing a geometric surface representation of any object in a specialized 3D software such as Maya or 3Ds Max. Artists create 3D models of characters, environments, and objects based on the concept art.
3D Texturing:
The process of creating and applying textures (colors and surface properties) to a 3D model is called 3D texturing. Before coming to the texture artist, 3D models are usually in a default shaded flat color. Textures are applied to 3D models to add surface details like color, roughness, or metalness.
3D Rigging:
Rigs are skeleton-like structures that allow animators to move characters and objects. During the rigging process, a bone structure is put into the 3D object so that the animators can move different parts of the geometric object (in character rigging, for example) as quickly and efficiently as possible.
3D Animation:
The movements of the 3D objects or characters in a scene or setting are created during the animation stage. Animators bring characters to life by creating movements, gestures, and expressions. Animation is usually the most crucial and time-consuming part of producing a 3D animated video.
VFX:
A 3D animator animates almost everything, but elements like hair, fur, water, fire, clothes, or dust; key-framing them would be too difficult or even impossible. Visual effects like fire, smoke, explosions, and magical elements are added.
Lighting:
Lighting sets the mood and highlights key elements. It’s critical for visual storytelling.
Rendering:
Final scenes are processed and converted into image sequences or video files. This step is resource-intensive.
Read Also: 10 Tips to Create Engaging Corporate Videos
What is the animation post-production process?
Post-production is where everything comes together into the final piece. At this stage, the final touches are added to the project to make it look polished and professional (the definition of polished and professional might differ in various projects, of course).
Post-production artists have a number of tools that can make up the look of a project in whatever way they want.
Compositing:
To make a final output, the layers rendered previously are put together again in compositing. Multiple rendered layers are combined to create the final frame. The layering process can be as simple as putting 2 layers together or as complex as matching hundreds of layers and adjusting their properties.
2D VFX:
Additional 2D effects like glows, overlays, and filters are applied. Some visual effects, such as sparks, dust, raindrops, camera shakes, et cetera, are more easily achieved in a 2D environment at the end of the project without sacrificing the quality. These effects are usually mixed with other layers in compositing.
Color correction:
Also known as color timing or color grading, color correction is literally the last adjustment we make to a 3D animation in the pipeline. Scenes are adjusted for color balance and mood consistency.
Final output:
The project is exported in required formats and resolutions for distribution. There are different options out there regarding the output format of the pipeline. However, the most common type is a digital video which is compatible with most digital devices and can be played on the internet.
What is the difference between 3D animation and CGI pipeline?
While 3D animation refers to the art of animating three-dimensional elements, CGI is a broader term that includes any computer-generated visual content. The 3D animation pipeline is a subset of the CGI pipeline. There’s no difference between CGI and 3D animation as both use the same techniques and methods to create and use art in different ways.
Why do we use a pipeline for 3D animation production?
You can picture the 3D animation pipeline as a creative assembly line in which everything is planned out, from conception to publishing. The entire pipeline might consist of as many as 500 artists or as few as 2.
The most significant point of having a workflow in place is that every single one of these artists must know what, when and how exactly the tasks in hand should be done and handed out to the next artist or group of artists.
Time management:
A structured pipeline avoids delays and sets clear timelines for each stage. There needs to be a detailed time frame for each step and a grand plan to coordinate multiple creative lines accordingly; some of which are supposed to be done simultaneously.
Budget management:
It helps monitor expenses and resource allocation effectively.
Team management:
Different teams can work in parallel without conflicts using clear roles and workflows.
Structuring and standardization:
A pipeline ensures consistency, especially in large-scale or long-term projects.
The AI Revolution in 3D Animation: 2025 Update
AI tools are transforming the 3D animation space. They can now auto-rig characters, enhance lip-sync, and even generate animation sequences based on scripts. In 2025, AI integration is improving productivity and reducing costs for studios worldwide.
How to get started in animation production (FAQ)
Let’s look at some of the questions that our readers have asked after reading our blog. We’ve listed the questions with short answers to get you going.
What do I need to get started in animation production?
You need a good computer, animation software (like Blender or Maya), and a solid understanding of the animation process.
Do you need to know how to draw to be a good animator?
While helpful, drawing is not mandatory for 3D animators. Understanding movement, timing, and storytelling is more critical.
How is animation a career?
Animation offers careers in film, TV, gaming, advertising, and more. It's a creative and technical profession with growing demand.
How do you make a great animation portfolio?
Show a variety of work: character animation, environments, VFX, and even unfinished sketches. Quality matters more than quantity.
Summary
The 3D animation pipeline is a structured approach to producing animated content. From pre-production planning to final output, each step ensures creative consistency and technical accuracy. With growing demand and the rise of AI, mastering this pipeline is crucial for anyone entering the animation industry.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 11
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.